Contact with nature can improve emotions, enhance cognitive function, and reduce stress to promote health. Understanding more about nature's impact on health can help us enhance our quality of life, propose strategies for land management, ecosystem conservation, and design cities, residences, and parks suitable for habitation. Current research on the health-promoting effects of nature largely focuses on the influence of natural landscapes, while studies on the olfactory system represent an emerging field.
To explore this new research direction, scholars from around the world gathered in California for the "Nature and Human Well-Being: The Olfactory Pathway" workshop. This interdisciplinary research group includes experts from fields such as anthropology, physiology, psychology, ecology, public health, atmospheric chemistry, and forestry, representing research institutions in the United States, United Kingdom, Taiwan, Germany, Poland, and Cyprus. The workshop's findings were published in Science Advances, proposing expanded research into "how natural scents and aromas influence human health and well-being."
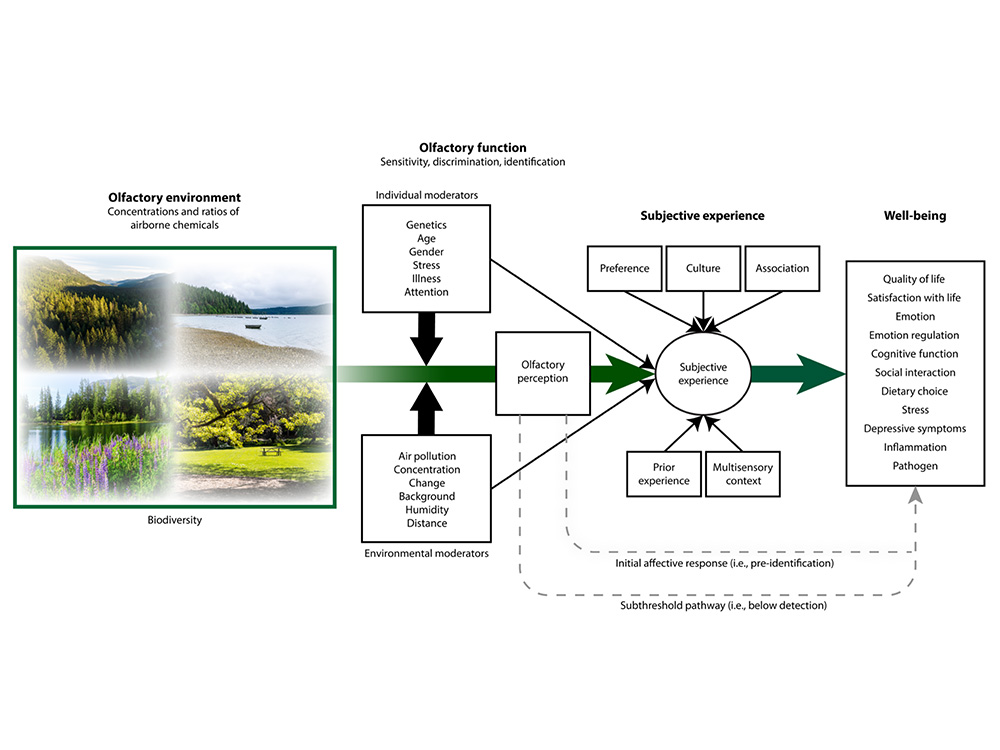
Human olfaction is fundamentally a complex chemical detection system. Whether in conscious or unconscious states, olfactory information is transmitted to the nervous system for interpretation, influencing health and well-being. Nature continually releases chemical compounds, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by plants, which keep the olfactory system engaged. These compounds can persist in the air for hours or days, affecting humans. Forests emit complex compounds into the air, influencing olfactory environments through atmospheric reactions and mixing. Moreover, olfactory messages are closely tied to specific memories or cultural and personal experiences, imbuing scents with different meanings.
This study proposes a conceptual framework to explain how natural olfactory environments affect human health and well-being:
- Olfactory environments are characterized by the concentration and proportion of chemicals in the air.
- Dimensions of olfactory function (sensitivity, discrimination, and identification) are influenced by various personal and environmental factors, collectively regulating olfactory perception.
- Subjective experience serves as an intermediary factor in olfactory perception leading to health outcomes, encompassing personal preferences, culture, associations, past experiences, and multisensory contexts.
- These pathways influence human health and well-being, impacting quality of life and satisfaction, emotional responses and regulation, cognitive function, and behavioral outcomes.
This research analyzes how natural environments affect human health and well-being through the olfactory system, urging further investigation into how human activities alter natural olfactory footprints — including pollution that changes or disrupts odors in the air.
Full Research Paper: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adn3028
Source: https://www.ntu.edu.tw/spotlight/2024/2273_20240522.html