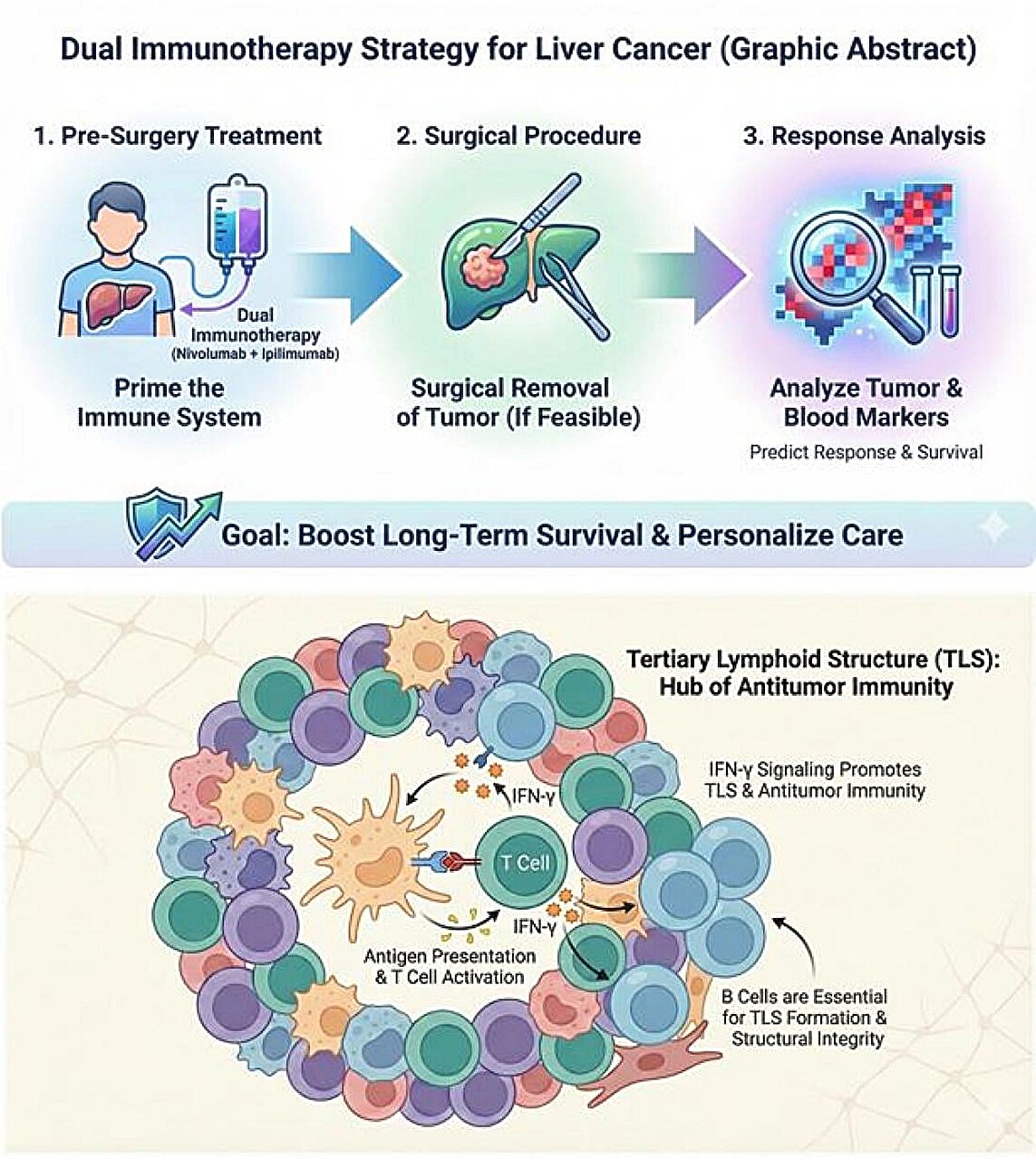
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy before surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may produce major pathological response in about one-third of the surgical patients. The clinical and pre-clinical research highlighted that the formation of organized immune hubs within the tumor (tertiary lymphoid structure) after ICI therapy is critical for the induction of antitumor immunity.
A multi-center clinical trial in Taiwan, sponsored by the National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan, demonstrates that combining the ICI nivolumab and ipilimumab before surgery may improve long-term outcomes for patients with potentially resectable HCC.
Among the 43 patients enrolled in the study, the estimated 4-year overall survival rate reached an encouraging 60%, with one-third of surgical patients achieving a major pathological response, meaning > 90% of tumor necrosis. This "neoadjuvant" approach effectively utilizes the time before the operation to prime the body's immune system, creating a more durable defense against the disease. The study is published in Journal of Hepatology.
"This neoadjuvant approach also provides valuable opportunity to explore how ICI therapy works," says co-corresponding author Prof. Chiun Hsu at Graduate Institute of Oncology, National Taiwan University.
The study team found that induction of interferon-gamma signaling and formation of "immune hubs"—technically known as tertiary lymphoid structures, in the tumor microenvironment by ICI therapy play critical roles in coordinating a powerful anti-cancer attack.
The research team also discovered that monitoring T cell "exhaustion" and activation in the patients' blood samples after ICI therapy may help doctors predict which patients are most likely to respond to the treatment. This sophisticated combination of tissue-level insights and blood-based tracking offers a promising new roadmap for the development of personalizing care for HCC patients.
To see article on Medical Xpress: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2026-01-immunotherapy-surgery-boosts-survival-liver.html